This has been demonstrated to occur experimentally via oxidation and hydrolysis at 22C and a pH of 2.5. Also in the capillary blood, which is often used for blood sugar determination, the values are sometimes higher than in the venous blood. [116] Recently, glucose has been gaining commercial use as a key component of "kits" containing lactic acid and insulin intended to induce hypoglycemia and hyperlactatemia to combat different cancers and infections. [83] The binding of glucose to the sweet receptor on the tongue induces a release of various hormones of energy metabolism, either through glucose or through other sugars, leading to an increased cellular uptake and lower blood sugar levels. [86] After food intake the blood sugar concentration increases. [122] Glucose boiled in an ammonium molybdate solution turns the solution blue. [38]:359 The free energy of formation of -d-glucose is 917.2 kilojoules per mole. Glucose and other monosaccharides rapidly produce a reddish color and reddish brown copper(I) oxide (Cu2O). Oligosaccharides of glucose combined with other sugars serve as important energy stores.
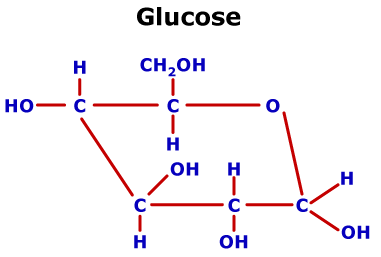
If there is not enough oxygen available for this, the glucose degradation in animals occurs anaerobic to lactate via lactic acid fermentation and releases much less energy.
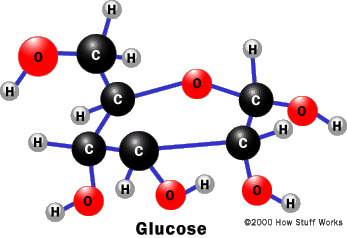
This is called the Warburg effect. It is also a precursor for the synthesis of other important molecules such as vitamin C (ascorbic acid). In anaerobic respiration, one glucose molecule produces a net gain of two ATP molecules (four ATP molecules are produced during glycolysis through substrate-level phosphorylation, but two are required by enzymes used during the process). Glucose can also degrade to form carbon dioxide through abiotic means. [129], Glucose can be quantified by copper iodometry.[133].


Glucose mainly comes from foodabout 300g (11oz) per day is produced by conversion of food,[45] but it is also synthesized from other metabolites in the body's cells.
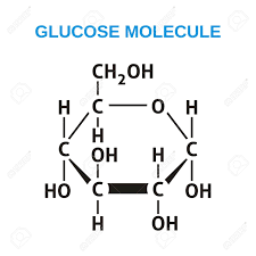
[40] In adult humans, there is about 18g (0.63oz) of glucose,[41] of which about 4g (0.14oz) is present in the blood. Thomas Becker, Dietmar Breithaupt, Horst Werner Doelle, Armin Fiechter, Gnther Schlegel, Sakayu Shimizu, Hideaki Yamada: World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, Lobry de BruynAlberdaVan Ekenstein transformation, "Rapport sur un mmoire de M. Pligiot, intitul: Recherches sur la nature et les proprits chimiques des sucres", "Experiences chimiques faites dans le dessein de tirer un veritable sucre de diverses plantes, qui croissent dans nos contres", "On Fischer's Classification of Stereo-Isomers.1", "Hans von Euler-Chelpin - Facts - NobelPrize.org", "Bernardo Houssay - Facts - NobelPrize.org", "Binary and ternary phenylboronic acid complexes with saccharides and Lewis bases", "High Blood Glucose and Diabetes Complications: The buildup of molecules known as AGEs may be the key link", "Glucose transporters: Physiological and pathological roles", "GLUT2, glucose sensing and glucose homeostasis", "Physiology of renal glucose handling via SGLT1, SGLT2, and GLUT2", "Chemistry for Biologists: Photosynthesis", "Aircraft Measurement of Organic Aerosols over China", "Glucose and gluconic acid oxidation of Pseudomonas saccharophila", "Roles of glucose transport and glucose phosphorylation in muscle insulin resistance of NIDDM", "Glucose transporters in cancer metabolism", "Electrochemical degradation of organic substances at PbO2 anodes: Monitoring by continuous CO2 measurements", "Chapter 3: Calculation of the Energy Content of Foods Energy Conversion Factors", "Pathway alignment: Application to the comparative analysis of glycolytic enzymes", "Blood Brain Barrier and Cerebral Metabolism (Section 4, Chapter 11)", "Self-Control Relies on Glucose as a Limited Energy Source: Willpower is More than a Metaphor", "Do non-nutritive sweeteners influence acute glucose homeostasis in humans? [84], The blood sugar content of a healthy person in the short-time fasting state, e.g. [136] Derivatization using silylation reagents is commonly used. Various sources of glucose, such as grape juice (for wine) or malt (for beer), are used for fermentation to ethanol during the production of alcoholic beverages. [106] The reaction is carried out at a pH = 4.65.2 and a temperature of 5560C. Values over 180mg/dL in venous whole blood are pathological and are termed hyperglycemia, values below 40mg/dL are termed hypoglycaemia. As a reducing sugar, glucose reacts in the Nylander's test. At physiological conditions, this initial reaction is irreversible. Individuals with diabetes or other conditions that result in low blood sugar often carry small amounts of sugar in various forms. The pancreas is the organ responsible for the secretion of the hormones insulin and glucagon. [55], In plants and some prokaryotes, glucose is a product of photosynthesis. In the liver about 150g (5.3oz) of glycogen are stored, in skeletal muscle about 250g (8.8oz). In other living organisms, other forms of fermentation can occur.

The enzyme glucose oxidase (GOx) converts glucose into gluconic acid and hydrogen peroxide while consuming oxygen. In particular, for the analysis of complex mixtures containing glucose, e.g. Glycogen is the body's "glucose energy storage" mechanism, because it is much more "space efficient" and less reactive than glucose itself. [53] Excess glucose is broken down and converted into fatty acids, which are stored as triglycerides. Presumably, glucose is the most abundant natural monosaccharide because it is less glycated with proteins than other monosaccharides.

Furthermore, for the cleavage of disaccharides, there are maltase, lactase, sucrase, trehalase, and others. [66] Furthermore, addition of the high-energy phosphate group activates glucose for subsequent breakdown in later steps of glycolysis. The test-strip method employs the above-mentioned enzymatic conversion of glucose to gluconic acid to form hydrogen peroxide. In the small intestine (more precisely, in the jejunum),[46] glucose is taken up into the intestinal epithelium with the help of glucose transporters[47] via a secondary active transport mechanism called sodium ion-glucose symport via sodium/glucose cotransporter 1 (SGLT1). The renal tubular cells can also produce glucose. Most soft drinks in the US use HFCS-55 (with a fructose content of 55% in the dry mass), while most other HFCS-sweetened foods in the US use HFCS-42 (with a fructose content of 42% in the dry mass). [38]:59 In some bacteria and, in modified form, also in archaea, glucose is degraded via the Entner-Doudoroff pathway.[65]. [125] The GOx is immobilized on the electrode surface or in a membrane placed close to the electrode. As a result of its importance in human health, glucose is an analyte in glucose tests that are common medical blood tests. These polymers, when consumed by animals, fungi and bacteria, are degraded to glucose using enzymes. Neurons, cells of the renal medulla and erythrocytes depend on glucose for their energy production. by the consumption of oxygen using fluorescence-optical sensors. [87] When needed, glucose is released into the bloodstream by glucose-6-phosphatase from glucose-6-phosphate originating from liver and kidney glycogen, thereby regulating the homeostasis of blood glucose concentration.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/galanthamine-58b5f0105f9b586046205716.gif)
[114] Typical chemical reactions of glucose when heated under water-free conditions are caramelization and, in presence of amino acids, the Maillard reaction. [63] In the further course of the metabolism, it can be completely degraded via oxidative decarboxylation, the citric acid cycle (synonym Krebs cycle) and the respiratory chain to water and carbon dioxide. [102]
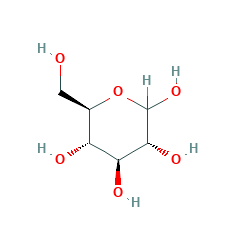
In the Tollens test, after addition of ammoniacal AgNO3 to the sample solution, glucose reduces Ag+ to elemental silver.[119]. In blood plasma, the measured values are about 1015% higher. Glucose also can be found outside of living organisms in the ambient environment. Insulin resistance occurs when the pancreas tries to produce more and more insulin in response to persistently elevated blood glucose levels. [121], Upon heating a dilute potassium hydroxide solution with glucose to 100C, a strong reddish browning and a caramel-like odor develops. [134][135] Taking into account the isotope ratios, it is also possible to reliably detect honey adulteration by added sugars with these methods. In living organisms, glucose is converted to several other chemical compounds that are the starting material for various metabolic pathways. [118] Due to mutarotation, glucose is always present to a small extent as an open-chain aldehyde.

[122] Concentrated sulfuric acid dissolves dry glucose without blackening at room temperature forming sugar sulfuric acid.

Blood glucose monitoring can be performed by multiple methods, such as the fasting glucose test which measures the level of glucose in the blood after 8 hours of fasting. [34] By adding acid or base, this transformation is much accelerated. 3: Iss.
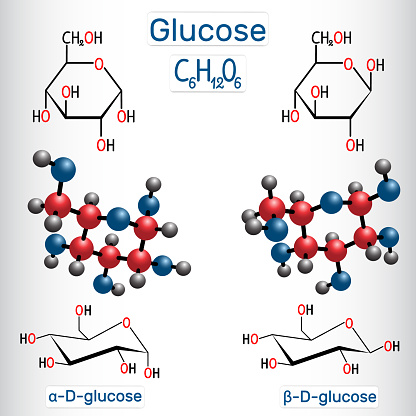
.mw-parser-output .citation{word-wrap:break-word}.mw-parser-output .citation:target{background-color:rgba(0,127,255,0.133)}^A The carbohydrate value is calculated in the USDA database and does not always correspond to the sum of the sugars, the starch, and the "dietary fiber". The metabolic pathway that begins with molecules containing two to four carbon atoms (C) and ends in the glucose molecule containing six carbon atoms is called gluconeogenesis and occurs in all living organisms.

Most dietary carbohydrates contain glucose, either as their only building block (as in the polysaccharides starch and glycogen), or together with another monosaccharide (as in the hetero-polysaccharides sucrose and lactose). [127] A particularly promising method is the so-called "enzyme wiring", where the electron flowing during the oxidation is transferred via a molecular wire directly from the enzyme to the electrode. The bacterium Escherichia coli can grow on nutrient media containing glucose as the sole carbon source. Benjamin Caballero, Paul Finglas, Fidel Toldr: Manfred Hesse, Herbert Meier, Bernd Zeeh, Stefan Bienz, Laurent Bigler, Thomas Fox: H. Robert Horton, Laurence A. Moran, K. Gray Scrimgeour, Marc D. Perry, J. David Rawn: W. A. Scherbaum, B. M. Lobnig, In: Hans-Peter Wolff, Thomas R. Weihrauch: Estela, Carlos (2011) "Blood Glucose Levels," Undergraduate Journal of Mathematical Modeling: One + Two: Vol. The cleavage of glycogen is termed glycogenolysis, the cleavage of starch is called starch degradation.[57]. [132] Finally, there are enzyme-based concepts that use the intrinsic absorbance or fluorescence of (fluorescence-labeled) enzymes as reporters. The amylases most often come from Bacillus licheniformis[104] or Bacillus subtilis (strain MN-385),[104] which are more thermostable than the originally used enzymes.

Glucose can also be converted from bacterial xylose isomerase to fructose. Glucose is produced by plants through photosynthesis using sunlight, water and carbon dioxide and can be used by all living organisms as an energy and carbon source. Some commercial glucose occurs as a component of invert sugar, a roughly 1:1 mixture of glucose and fructose that is produced from sucrose. [122] In an ammoniacal silver solution, glucose (as well as lactose and dextrin) leads to the deposition of silver.
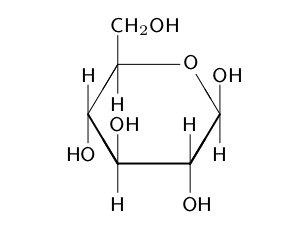
These include lactose, the predominant sugar in milk, which is a glucose-galactose disaccharide, and sucrose, another disaccharide which is composed of glucose and fructose. [103] This is the reason for the former common name "starch sugar". [112] In Mexico, on the other hand, soft drinks are sweetened by cane sugar, which has a higher sweetening power.
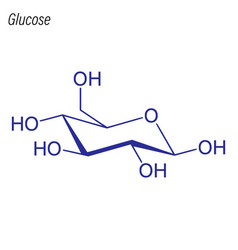
One sugar commonly used is glucose, often in the form of glucose tablets (glucose pressed into a tablet shape sometimes with one or more other ingredients as a binder), hard candy, or sugar packet. [103] When made from corn syrup, the final product is high-fructose corn syrup (HFCS). [82], The glucose in the blood is called blood sugar. [54] About 90% of kidney glucose reabsorption is via SGLT2 and about 3% via SGLT1. InChI=1S/C6H12O6/c7-1-2-3(8)4(9)5(10)6(11)12-2/h2-11H,1H2/t2-,3-,4+,5-,6?/m1/s1, C([C@@H]1[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]([C@H](O1)O)O)O)O)O, Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their, Classical qualitative detection reactions, Photometric enzymatic methods in solution. A solution with indigo carmine and sodium carbonate destains when boiled with glucose.[122]. [83] In addition, glucose in the brain binds to glucose receptors of the reward system in the nucleus accumbens. [104][105] Starting in 1982, pullulanases from Aspergillus niger were used in the production of glucose syrup to convert amylopectin to starch (amylose), thereby increasing the yield of glucose. In addition, glucose metabolites produce all nonessential amino acids, sugar alcohols such as mannitol and sorbitol, fatty acids, cholesterol and nucleic acids. PINs are not identified for natural products. [122] An alkaline bismuth solution is used to precipitate elemental, black-brown bismuth with glucose. Some of these polymers (starch or glycogen) serve as energy stores, while others (cellulose and chitin, which is made from a derivative of glucose) have structural roles. Encyclopedia.com. A systematic review", "Diagnosing Diabetes and Learning About Prediabetes", "An insulin index of foods: The insulin demand generated by 1000-kJ portions of common foods", "Pancreatic Regulation of Glucose Homeostasis", "A syn-ent-labdadiene derivative with a rare spiro--lactone function from the male cones of Wollemia nobilis", "Triterpene Saponins from the Roots ofIlex asprella", "High Fructose Corn Syrup: Questions and Answers", "A Glucose-Triptolide Conjugate Selectively Targets Cancer Cells under Hypoxia", Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft, "Ueber die Nachweisung des Traubenzuckers neben Dextrin und verwandten Krpern", "Review of glucose oxidases and glucose dehydrogenases: A bird's eye view of glucose sensing enzymes", Max Planck Institute of Molecular Plant Physiology, "Sweetening pharmaceutical radiochemistry by (18)f-fluoroglycosylation: A short review", Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase deficiency, Slavery in the British and French Caribbean, https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Glucose&oldid=1100590585, World Health Organization essential medicines, Articles with German-language sources (de), Short description is different from Wikidata, Chemical articles with multiple compound IDs, Multiple chemicals in an infobox that need indexing, Chemical articles with multiple CAS registry numbers, Pages using collapsible list with both background and text-align in titlestyle, Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes, Articles containing Ancient Greek (to 1453)-language text, Pages using multiple image with manual scaled images, All articles needing additional references, Articles needing additional references from April 2022, Wikipedia articles needing factual verification from April 2022, Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License 3.0, This page was last edited on 26 July 2022, at 18:19. [78][79][80][81] In the brain, which is dependent on glucose and oxygen as the major source of energy, the glucose concentration is usually 4 to 6mM (5mM equals 90mg/dL),[41] but decreases to 2 to 3mM when fasting. Over time the blood glucose levels should decrease as insulin allows it to be taken up by cells and exit the blood stream. The main reason for the immediate phosphorylation of glucose is to prevent its diffusion out of the cell as the charged phosphate group prevents glucose 6-phosphate from easily crossing the cell membrane.

Ultimately almost all biomolecules come from the assimilation of carbon dioxide in plants and microbes during photosynthesis.
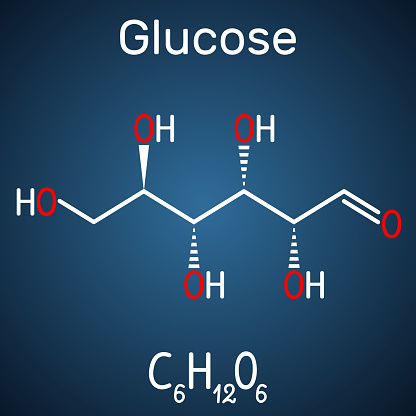
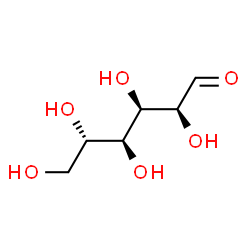
[50] In addition to the phosphorylation to glucose-6-phosphate, which is part of the glycolysis, glucose can be oxidized during its degradation to glucono-1,5-lactone. This is often critical for their functioning. In addition to the reaction of phenol with 4-aminoantipyrine, new chromogenic reactions have been developed that allow photometry at higher wavelengths (550nm, 750nm).

[89] Eating or fasting prior to taking a blood sample has an effect on analyses for glucose in the blood; a high fasting glucose blood sugar level may be a sign of prediabetes or diabetes mellitus.[90]. Glucose is mainly used for the production of fructose and of glucose-containing foods. concanavalin A) as a receptor. Gluconeogenesis allows the organism to build up glucose from other metabolites, including lactate or certain amino acids, while consuming energy. [129][130] Given the importance of glucose analysis in the life sciences, numerous optical probes have also been developed for saccharides based on the use of boronic acids,[131] which are particularly useful for intracellular sensory applications where other (optical) methods are not or only conditionally usable. Glucose is the human body's key source of energy, through aerobic respiration, providing about 3.75kilocalories (16kilojoules) of food energy per gram. [97] Unbound glucose is one of the main ingredients of honey.

The reagents are immobilised on a polymer matrix, the so-called test strip, which assumes a more or less intense color. [137] Also, the proportions of di- and trisaccharides can be quantified. Another enzyme, peroxidase, catalyzes a chromogenic reaction (Trinder reaction)[123] of phenol with 4-aminoantipyrine to a purple dye. For example, glucose concentrations in atmospheric air from inland China range from 0.8-20.1 pg/l, whereas east coastal China glucose concentrations range from 10.3-142 pg/l.[60]. [59] However, the glucose released in muscle cells upon cleavage of the glycogen can not be delivered to the circulation because glucose is phosphorylated by the hexokinase, and a glucose-6-phosphatase is not expressed to remove the phosphate group. Without it, glucose cannot enter the cell and therefore cannot be used as fuel for the body's functions. In principle, cellulose could be hydrolyzed to glucose, but this process is not yet commercially practical.[26]. Precious metals such as platinum or gold are used in electrodes, as well as carbon nanotube electrodes, which e.g. [82] Confusion occurs below 1mM and coma at lower levels. However, most glucose does not occur in its free form, but in the form of its polymers, i.e. [95] Insulin is a hormone that regulates glucose levels, allowing the body's cells to absorb and use glucose. [56] Glucose is also formed by the breakdown of polymeric forms of glucose like glycogen (in animals and mushrooms) or starch (in plants). in glycated hemoglobin. [122] With Hager's reagent, glucose forms mercury oxide during boiling. Liver cell glycogen can be converted to glucose and returned to the blood when insulin is low or absent; muscle cell glycogen is not returned to the blood because of a lack of enzymes. [117]. [126] CuCuO nanowires are also used as enzyme-free amperometric electrodes, reaching a detection limit of 50mol/L. The names of the degrading enzymes are often derived from the particular poly- and disaccharide; inter alia, for the degradation of polysaccharide chains there are amylases (named after amylose, a component of starch), cellulases (named after cellulose), chitinases (named after chitin), and more. [124], The electroanalysis of glucose is also based on the enzymatic reaction mentioned above.

For the increased uptake of glucose in tumors various SGLT and GLUT are overly produced.[70][71]. The first step of glycolysis is the phosphorylation of glucose by a hexokinase to form glucose 6-phosphate. [42] Approximately 180220g (6.37.8oz) of glucose is produced in the liver of an adult in 24 hours.

The produced hydrogen peroxide can be amperometrically quantified by anodic oxidation at a potential of 600 mV. This complex of the proteins T1R2 and T1R3 makes it possible to identify glucose-containing food sources.
Wenyue Kang and Zhijun Zhang (2020): "Selective Production of Acetic Acid via Catalytic Fast Pyrolysis of Hexoses over Potassium Salts", "glucose." Glucose is also added onto certain proteins and lipids in a process called glycosylation. Use of glucose as an energy source in cells is by either aerobic respiration, anaerobic respiration, or fermentation. [83][85] Insulin lowers the glucose level, glucagon increases it. Glucose is produced industrially from starch by enzymatic hydrolysis using glucose amylase or by the use of acids. In concentrated solutions of glucose with a low proportion of other carbohydrates, its concentration can be determined with a polarimeter. Glucose uptake in cells of organisms is measured with 2-deoxy-D-glucose or fluorodeoxyglucose. [122][verification needed] In a yeast solution, alcoholic fermentation produces carbon dioxide in the ratio of 2.0454 molecules of glucose to one molecule of CO2.

In humans, about 70 genes are known that code for glycosidases. In dilute sodium hydroxide or other dilute bases, the monosaccharides mannose, glucose and fructose interconvert (via a Lobry de BruynAlberdaVan Ekenstein transformation), so that a balance between these isomers is formed. To monitor the body's response to blood glucose-lowering therapy, glucose levels can be measured. In the US, almost exclusively corn (more precisely, corn syrup) is used as glucose source for the production of isoglucose, which is a mixture of glucose and fructose, since fructose has a higher sweetening power with same physiological calorific value of 374 kilocalories per 100 g. The annual world production of isoglucose is 8 million tonnes (as of 2011). [38]:59 In humans, gluconeogenesis occurs in the liver and kidney,[58] but also in other cell types. [41], Many of the long-term complications of diabetes (e.g., blindness, kidney failure, and peripheral neuropathy) are probably due to the glycation of proteins or lipids.

g). Humans do not produce cellulases, chitinases, or trehalases, but the bacteria in the gut microbiota do. [ 1], Tumor cells often grow comparatively quickly and consume an above-average amount of glucose by glycolysis,[69] which leads to the formation of lactate, the end product of fermentation in mammals, even in the presence of oxygen. This negative spiral contributes to pancreatic burnout, and the disease progression of diabetes.
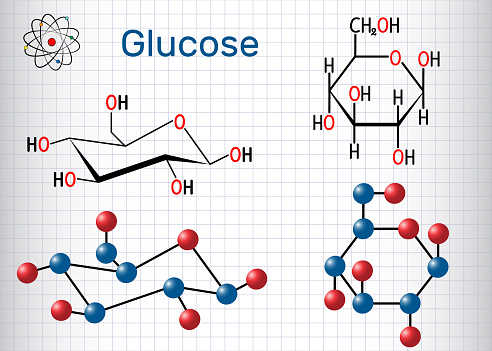
With a high supply of glucose, the metabolite acetyl-CoA from the Krebs cycle can also be used for fatty acid synthesis. after overnight fasting, is about 70 to 100mg/dL of blood (4 to 5.5mM). It is used as an energy source in organisms, from bacteria to humans, through either aerobic respiration, anaerobic respiration (in bacteria), or fermentation. Other than its direct use as a monomer, glucose can be broken down to synthesize a wide variety of other biomolecules. [49] Glucose enters the liver via the portal vein and is stored there as a cellular glycogen. In addition, the values in the arterial blood are higher than the concentrations in the venous blood since glucose is absorbed into the tissue during the passage of the capillary bed. In an ammoniacal lead acetate solution, white lead glycoside is formed in the presence of glucose, which becomes less soluble on cooking and turns brown. [75] The high availability of carbohydrates from plant biomass has led to a variety of methods during evolution, especially in microorganisms, to utilize glucose for energy and carbon storage. [76], Glucose and oxygen supply almost all the energy for the brain,[77] so its availability influences psychological processes.
 If there is not enough oxygen available for this, the glucose degradation in animals occurs anaerobic to lactate via lactic acid fermentation and releases much less energy.
If there is not enough oxygen available for this, the glucose degradation in animals occurs anaerobic to lactate via lactic acid fermentation and releases much less energy.  This is called the Warburg effect. It is also a precursor for the synthesis of other important molecules such as vitamin C (ascorbic acid). In anaerobic respiration, one glucose molecule produces a net gain of two ATP molecules (four ATP molecules are produced during glycolysis through substrate-level phosphorylation, but two are required by enzymes used during the process). Glucose can also degrade to form carbon dioxide through abiotic means. [129], Glucose can be quantified by copper iodometry.[133].
This is called the Warburg effect. It is also a precursor for the synthesis of other important molecules such as vitamin C (ascorbic acid). In anaerobic respiration, one glucose molecule produces a net gain of two ATP molecules (four ATP molecules are produced during glycolysis through substrate-level phosphorylation, but two are required by enzymes used during the process). Glucose can also degrade to form carbon dioxide through abiotic means. [129], Glucose can be quantified by copper iodometry.[133]. 
 Glucose mainly comes from foodabout 300g (11oz) per day is produced by conversion of food,[45] but it is also synthesized from other metabolites in the body's cells.
Glucose mainly comes from foodabout 300g (11oz) per day is produced by conversion of food,[45] but it is also synthesized from other metabolites in the body's cells.  [40] In adult humans, there is about 18g (0.63oz) of glucose,[41] of which about 4g (0.14oz) is present in the blood. Thomas Becker, Dietmar Breithaupt, Horst Werner Doelle, Armin Fiechter, Gnther Schlegel, Sakayu Shimizu, Hideaki Yamada: World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, Lobry de BruynAlberdaVan Ekenstein transformation, "Rapport sur un mmoire de M. Pligiot, intitul: Recherches sur la nature et les proprits chimiques des sucres", "Experiences chimiques faites dans le dessein de tirer un veritable sucre de diverses plantes, qui croissent dans nos contres", "On Fischer's Classification of Stereo-Isomers.1", "Hans von Euler-Chelpin - Facts - NobelPrize.org", "Bernardo Houssay - Facts - NobelPrize.org", "Binary and ternary phenylboronic acid complexes with saccharides and Lewis bases", "High Blood Glucose and Diabetes Complications: The buildup of molecules known as AGEs may be the key link", "Glucose transporters: Physiological and pathological roles", "GLUT2, glucose sensing and glucose homeostasis", "Physiology of renal glucose handling via SGLT1, SGLT2, and GLUT2", "Chemistry for Biologists: Photosynthesis", "Aircraft Measurement of Organic Aerosols over China", "Glucose and gluconic acid oxidation of Pseudomonas saccharophila", "Roles of glucose transport and glucose phosphorylation in muscle insulin resistance of NIDDM", "Glucose transporters in cancer metabolism", "Electrochemical degradation of organic substances at PbO2 anodes: Monitoring by continuous CO2 measurements", "Chapter 3: Calculation of the Energy Content of Foods Energy Conversion Factors", "Pathway alignment: Application to the comparative analysis of glycolytic enzymes", "Blood Brain Barrier and Cerebral Metabolism (Section 4, Chapter 11)", "Self-Control Relies on Glucose as a Limited Energy Source: Willpower is More than a Metaphor", "Do non-nutritive sweeteners influence acute glucose homeostasis in humans? [84], The blood sugar content of a healthy person in the short-time fasting state, e.g. [136] Derivatization using silylation reagents is commonly used. Various sources of glucose, such as grape juice (for wine) or malt (for beer), are used for fermentation to ethanol during the production of alcoholic beverages. [106] The reaction is carried out at a pH = 4.65.2 and a temperature of 5560C. Values over 180mg/dL in venous whole blood are pathological and are termed hyperglycemia, values below 40mg/dL are termed hypoglycaemia. As a reducing sugar, glucose reacts in the Nylander's test. At physiological conditions, this initial reaction is irreversible. Individuals with diabetes or other conditions that result in low blood sugar often carry small amounts of sugar in various forms. The pancreas is the organ responsible for the secretion of the hormones insulin and glucagon. [55], In plants and some prokaryotes, glucose is a product of photosynthesis. In the liver about 150g (5.3oz) of glycogen are stored, in skeletal muscle about 250g (8.8oz). In other living organisms, other forms of fermentation can occur.
[40] In adult humans, there is about 18g (0.63oz) of glucose,[41] of which about 4g (0.14oz) is present in the blood. Thomas Becker, Dietmar Breithaupt, Horst Werner Doelle, Armin Fiechter, Gnther Schlegel, Sakayu Shimizu, Hideaki Yamada: World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, Lobry de BruynAlberdaVan Ekenstein transformation, "Rapport sur un mmoire de M. Pligiot, intitul: Recherches sur la nature et les proprits chimiques des sucres", "Experiences chimiques faites dans le dessein de tirer un veritable sucre de diverses plantes, qui croissent dans nos contres", "On Fischer's Classification of Stereo-Isomers.1", "Hans von Euler-Chelpin - Facts - NobelPrize.org", "Bernardo Houssay - Facts - NobelPrize.org", "Binary and ternary phenylboronic acid complexes with saccharides and Lewis bases", "High Blood Glucose and Diabetes Complications: The buildup of molecules known as AGEs may be the key link", "Glucose transporters: Physiological and pathological roles", "GLUT2, glucose sensing and glucose homeostasis", "Physiology of renal glucose handling via SGLT1, SGLT2, and GLUT2", "Chemistry for Biologists: Photosynthesis", "Aircraft Measurement of Organic Aerosols over China", "Glucose and gluconic acid oxidation of Pseudomonas saccharophila", "Roles of glucose transport and glucose phosphorylation in muscle insulin resistance of NIDDM", "Glucose transporters in cancer metabolism", "Electrochemical degradation of organic substances at PbO2 anodes: Monitoring by continuous CO2 measurements", "Chapter 3: Calculation of the Energy Content of Foods Energy Conversion Factors", "Pathway alignment: Application to the comparative analysis of glycolytic enzymes", "Blood Brain Barrier and Cerebral Metabolism (Section 4, Chapter 11)", "Self-Control Relies on Glucose as a Limited Energy Source: Willpower is More than a Metaphor", "Do non-nutritive sweeteners influence acute glucose homeostasis in humans? [84], The blood sugar content of a healthy person in the short-time fasting state, e.g. [136] Derivatization using silylation reagents is commonly used. Various sources of glucose, such as grape juice (for wine) or malt (for beer), are used for fermentation to ethanol during the production of alcoholic beverages. [106] The reaction is carried out at a pH = 4.65.2 and a temperature of 5560C. Values over 180mg/dL in venous whole blood are pathological and are termed hyperglycemia, values below 40mg/dL are termed hypoglycaemia. As a reducing sugar, glucose reacts in the Nylander's test. At physiological conditions, this initial reaction is irreversible. Individuals with diabetes or other conditions that result in low blood sugar often carry small amounts of sugar in various forms. The pancreas is the organ responsible for the secretion of the hormones insulin and glucagon. [55], In plants and some prokaryotes, glucose is a product of photosynthesis. In the liver about 150g (5.3oz) of glycogen are stored, in skeletal muscle about 250g (8.8oz). In other living organisms, other forms of fermentation can occur.  The enzyme glucose oxidase (GOx) converts glucose into gluconic acid and hydrogen peroxide while consuming oxygen. In particular, for the analysis of complex mixtures containing glucose, e.g. Glycogen is the body's "glucose energy storage" mechanism, because it is much more "space efficient" and less reactive than glucose itself. [53] Excess glucose is broken down and converted into fatty acids, which are stored as triglycerides. Presumably, glucose is the most abundant natural monosaccharide because it is less glycated with proteins than other monosaccharides.
The enzyme glucose oxidase (GOx) converts glucose into gluconic acid and hydrogen peroxide while consuming oxygen. In particular, for the analysis of complex mixtures containing glucose, e.g. Glycogen is the body's "glucose energy storage" mechanism, because it is much more "space efficient" and less reactive than glucose itself. [53] Excess glucose is broken down and converted into fatty acids, which are stored as triglycerides. Presumably, glucose is the most abundant natural monosaccharide because it is less glycated with proteins than other monosaccharides.  Furthermore, for the cleavage of disaccharides, there are maltase, lactase, sucrase, trehalase, and others. [66] Furthermore, addition of the high-energy phosphate group activates glucose for subsequent breakdown in later steps of glycolysis. The test-strip method employs the above-mentioned enzymatic conversion of glucose to gluconic acid to form hydrogen peroxide. In the small intestine (more precisely, in the jejunum),[46] glucose is taken up into the intestinal epithelium with the help of glucose transporters[47] via a secondary active transport mechanism called sodium ion-glucose symport via sodium/glucose cotransporter 1 (SGLT1). The renal tubular cells can also produce glucose. Most soft drinks in the US use HFCS-55 (with a fructose content of 55% in the dry mass), while most other HFCS-sweetened foods in the US use HFCS-42 (with a fructose content of 42% in the dry mass). [38]:59 In some bacteria and, in modified form, also in archaea, glucose is degraded via the Entner-Doudoroff pathway.[65]. [125] The GOx is immobilized on the electrode surface or in a membrane placed close to the electrode. As a result of its importance in human health, glucose is an analyte in glucose tests that are common medical blood tests. These polymers, when consumed by animals, fungi and bacteria, are degraded to glucose using enzymes. Neurons, cells of the renal medulla and erythrocytes depend on glucose for their energy production. by the consumption of oxygen using fluorescence-optical sensors. [87] When needed, glucose is released into the bloodstream by glucose-6-phosphatase from glucose-6-phosphate originating from liver and kidney glycogen, thereby regulating the homeostasis of blood glucose concentration.
Furthermore, for the cleavage of disaccharides, there are maltase, lactase, sucrase, trehalase, and others. [66] Furthermore, addition of the high-energy phosphate group activates glucose for subsequent breakdown in later steps of glycolysis. The test-strip method employs the above-mentioned enzymatic conversion of glucose to gluconic acid to form hydrogen peroxide. In the small intestine (more precisely, in the jejunum),[46] glucose is taken up into the intestinal epithelium with the help of glucose transporters[47] via a secondary active transport mechanism called sodium ion-glucose symport via sodium/glucose cotransporter 1 (SGLT1). The renal tubular cells can also produce glucose. Most soft drinks in the US use HFCS-55 (with a fructose content of 55% in the dry mass), while most other HFCS-sweetened foods in the US use HFCS-42 (with a fructose content of 42% in the dry mass). [38]:59 In some bacteria and, in modified form, also in archaea, glucose is degraded via the Entner-Doudoroff pathway.[65]. [125] The GOx is immobilized on the electrode surface or in a membrane placed close to the electrode. As a result of its importance in human health, glucose is an analyte in glucose tests that are common medical blood tests. These polymers, when consumed by animals, fungi and bacteria, are degraded to glucose using enzymes. Neurons, cells of the renal medulla and erythrocytes depend on glucose for their energy production. by the consumption of oxygen using fluorescence-optical sensors. [87] When needed, glucose is released into the bloodstream by glucose-6-phosphatase from glucose-6-phosphate originating from liver and kidney glycogen, thereby regulating the homeostasis of blood glucose concentration. :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/galanthamine-58b5f0105f9b586046205716.gif) [114] Typical chemical reactions of glucose when heated under water-free conditions are caramelization and, in presence of amino acids, the Maillard reaction. [63] In the further course of the metabolism, it can be completely degraded via oxidative decarboxylation, the citric acid cycle (synonym Krebs cycle) and the respiratory chain to water and carbon dioxide. [102]
[114] Typical chemical reactions of glucose when heated under water-free conditions are caramelization and, in presence of amino acids, the Maillard reaction. [63] In the further course of the metabolism, it can be completely degraded via oxidative decarboxylation, the citric acid cycle (synonym Krebs cycle) and the respiratory chain to water and carbon dioxide. [102]  In the Tollens test, after addition of ammoniacal AgNO3 to the sample solution, glucose reduces Ag+ to elemental silver.[119]. In blood plasma, the measured values are about 1015% higher. Glucose also can be found outside of living organisms in the ambient environment. Insulin resistance occurs when the pancreas tries to produce more and more insulin in response to persistently elevated blood glucose levels. [121], Upon heating a dilute potassium hydroxide solution with glucose to 100C, a strong reddish browning and a caramel-like odor develops. [134][135] Taking into account the isotope ratios, it is also possible to reliably detect honey adulteration by added sugars with these methods. In living organisms, glucose is converted to several other chemical compounds that are the starting material for various metabolic pathways. [118] Due to mutarotation, glucose is always present to a small extent as an open-chain aldehyde.
In the Tollens test, after addition of ammoniacal AgNO3 to the sample solution, glucose reduces Ag+ to elemental silver.[119]. In blood plasma, the measured values are about 1015% higher. Glucose also can be found outside of living organisms in the ambient environment. Insulin resistance occurs when the pancreas tries to produce more and more insulin in response to persistently elevated blood glucose levels. [121], Upon heating a dilute potassium hydroxide solution with glucose to 100C, a strong reddish browning and a caramel-like odor develops. [134][135] Taking into account the isotope ratios, it is also possible to reliably detect honey adulteration by added sugars with these methods. In living organisms, glucose is converted to several other chemical compounds that are the starting material for various metabolic pathways. [118] Due to mutarotation, glucose is always present to a small extent as an open-chain aldehyde.  Blood glucose monitoring can be performed by multiple methods, such as the fasting glucose test which measures the level of glucose in the blood after 8 hours of fasting. [34] By adding acid or base, this transformation is much accelerated. 3: Iss.
Blood glucose monitoring can be performed by multiple methods, such as the fasting glucose test which measures the level of glucose in the blood after 8 hours of fasting. [34] By adding acid or base, this transformation is much accelerated. 3: Iss.  .mw-parser-output .citation{word-wrap:break-word}.mw-parser-output .citation:target{background-color:rgba(0,127,255,0.133)}^A The carbohydrate value is calculated in the USDA database and does not always correspond to the sum of the sugars, the starch, and the "dietary fiber". The metabolic pathway that begins with molecules containing two to four carbon atoms (C) and ends in the glucose molecule containing six carbon atoms is called gluconeogenesis and occurs in all living organisms.
.mw-parser-output .citation{word-wrap:break-word}.mw-parser-output .citation:target{background-color:rgba(0,127,255,0.133)}^A The carbohydrate value is calculated in the USDA database and does not always correspond to the sum of the sugars, the starch, and the "dietary fiber". The metabolic pathway that begins with molecules containing two to four carbon atoms (C) and ends in the glucose molecule containing six carbon atoms is called gluconeogenesis and occurs in all living organisms.  Most dietary carbohydrates contain glucose, either as their only building block (as in the polysaccharides starch and glycogen), or together with another monosaccharide (as in the hetero-polysaccharides sucrose and lactose). [127] A particularly promising method is the so-called "enzyme wiring", where the electron flowing during the oxidation is transferred via a molecular wire directly from the enzyme to the electrode. The bacterium Escherichia coli can grow on nutrient media containing glucose as the sole carbon source. Benjamin Caballero, Paul Finglas, Fidel Toldr: Manfred Hesse, Herbert Meier, Bernd Zeeh, Stefan Bienz, Laurent Bigler, Thomas Fox: H. Robert Horton, Laurence A. Moran, K. Gray Scrimgeour, Marc D. Perry, J. David Rawn: W. A. Scherbaum, B. M. Lobnig, In: Hans-Peter Wolff, Thomas R. Weihrauch: Estela, Carlos (2011) "Blood Glucose Levels," Undergraduate Journal of Mathematical Modeling: One + Two: Vol. The cleavage of glycogen is termed glycogenolysis, the cleavage of starch is called starch degradation.[57]. [132] Finally, there are enzyme-based concepts that use the intrinsic absorbance or fluorescence of (fluorescence-labeled) enzymes as reporters. The amylases most often come from Bacillus licheniformis[104] or Bacillus subtilis (strain MN-385),[104] which are more thermostable than the originally used enzymes.
Most dietary carbohydrates contain glucose, either as their only building block (as in the polysaccharides starch and glycogen), or together with another monosaccharide (as in the hetero-polysaccharides sucrose and lactose). [127] A particularly promising method is the so-called "enzyme wiring", where the electron flowing during the oxidation is transferred via a molecular wire directly from the enzyme to the electrode. The bacterium Escherichia coli can grow on nutrient media containing glucose as the sole carbon source. Benjamin Caballero, Paul Finglas, Fidel Toldr: Manfred Hesse, Herbert Meier, Bernd Zeeh, Stefan Bienz, Laurent Bigler, Thomas Fox: H. Robert Horton, Laurence A. Moran, K. Gray Scrimgeour, Marc D. Perry, J. David Rawn: W. A. Scherbaum, B. M. Lobnig, In: Hans-Peter Wolff, Thomas R. Weihrauch: Estela, Carlos (2011) "Blood Glucose Levels," Undergraduate Journal of Mathematical Modeling: One + Two: Vol. The cleavage of glycogen is termed glycogenolysis, the cleavage of starch is called starch degradation.[57]. [132] Finally, there are enzyme-based concepts that use the intrinsic absorbance or fluorescence of (fluorescence-labeled) enzymes as reporters. The amylases most often come from Bacillus licheniformis[104] or Bacillus subtilis (strain MN-385),[104] which are more thermostable than the originally used enzymes.  Glucose can also be converted from bacterial xylose isomerase to fructose. Glucose is produced by plants through photosynthesis using sunlight, water and carbon dioxide and can be used by all living organisms as an energy and carbon source. Some commercial glucose occurs as a component of invert sugar, a roughly 1:1 mixture of glucose and fructose that is produced from sucrose. [122] In an ammoniacal silver solution, glucose (as well as lactose and dextrin) leads to the deposition of silver.
Glucose can also be converted from bacterial xylose isomerase to fructose. Glucose is produced by plants through photosynthesis using sunlight, water and carbon dioxide and can be used by all living organisms as an energy and carbon source. Some commercial glucose occurs as a component of invert sugar, a roughly 1:1 mixture of glucose and fructose that is produced from sucrose. [122] In an ammoniacal silver solution, glucose (as well as lactose and dextrin) leads to the deposition of silver.  These include lactose, the predominant sugar in milk, which is a glucose-galactose disaccharide, and sucrose, another disaccharide which is composed of glucose and fructose. [103] This is the reason for the former common name "starch sugar". [112] In Mexico, on the other hand, soft drinks are sweetened by cane sugar, which has a higher sweetening power.
These include lactose, the predominant sugar in milk, which is a glucose-galactose disaccharide, and sucrose, another disaccharide which is composed of glucose and fructose. [103] This is the reason for the former common name "starch sugar". [112] In Mexico, on the other hand, soft drinks are sweetened by cane sugar, which has a higher sweetening power.  One sugar commonly used is glucose, often in the form of glucose tablets (glucose pressed into a tablet shape sometimes with one or more other ingredients as a binder), hard candy, or sugar packet. [103] When made from corn syrup, the final product is high-fructose corn syrup (HFCS). [82], The glucose in the blood is called blood sugar. [54] About 90% of kidney glucose reabsorption is via SGLT2 and about 3% via SGLT1. InChI=1S/C6H12O6/c7-1-2-3(8)4(9)5(10)6(11)12-2/h2-11H,1H2/t2-,3-,4+,5-,6?/m1/s1, C([C@@H]1[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]([C@H](O1)O)O)O)O)O, Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their, Classical qualitative detection reactions, Photometric enzymatic methods in solution. A solution with indigo carmine and sodium carbonate destains when boiled with glucose.[122]. [83] In addition, glucose in the brain binds to glucose receptors of the reward system in the nucleus accumbens. [104][105] Starting in 1982, pullulanases from Aspergillus niger were used in the production of glucose syrup to convert amylopectin to starch (amylose), thereby increasing the yield of glucose. In addition, glucose metabolites produce all nonessential amino acids, sugar alcohols such as mannitol and sorbitol, fatty acids, cholesterol and nucleic acids. PINs are not identified for natural products. [122] An alkaline bismuth solution is used to precipitate elemental, black-brown bismuth with glucose. Some of these polymers (starch or glycogen) serve as energy stores, while others (cellulose and chitin, which is made from a derivative of glucose) have structural roles. Encyclopedia.com. A systematic review", "Diagnosing Diabetes and Learning About Prediabetes", "An insulin index of foods: The insulin demand generated by 1000-kJ portions of common foods", "Pancreatic Regulation of Glucose Homeostasis", "A syn-ent-labdadiene derivative with a rare spiro--lactone function from the male cones of Wollemia nobilis", "Triterpene Saponins from the Roots ofIlex asprella", "High Fructose Corn Syrup: Questions and Answers", "A Glucose-Triptolide Conjugate Selectively Targets Cancer Cells under Hypoxia", Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft, "Ueber die Nachweisung des Traubenzuckers neben Dextrin und verwandten Krpern", "Review of glucose oxidases and glucose dehydrogenases: A bird's eye view of glucose sensing enzymes", Max Planck Institute of Molecular Plant Physiology, "Sweetening pharmaceutical radiochemistry by (18)f-fluoroglycosylation: A short review", Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase deficiency, Slavery in the British and French Caribbean, https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Glucose&oldid=1100590585, World Health Organization essential medicines, Articles with German-language sources (de), Short description is different from Wikidata, Chemical articles with multiple compound IDs, Multiple chemicals in an infobox that need indexing, Chemical articles with multiple CAS registry numbers, Pages using collapsible list with both background and text-align in titlestyle, Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes, Articles containing Ancient Greek (to 1453)-language text, Pages using multiple image with manual scaled images, All articles needing additional references, Articles needing additional references from April 2022, Wikipedia articles needing factual verification from April 2022, Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License 3.0, This page was last edited on 26 July 2022, at 18:19. [78][79][80][81] In the brain, which is dependent on glucose and oxygen as the major source of energy, the glucose concentration is usually 4 to 6mM (5mM equals 90mg/dL),[41] but decreases to 2 to 3mM when fasting. Over time the blood glucose levels should decrease as insulin allows it to be taken up by cells and exit the blood stream. The main reason for the immediate phosphorylation of glucose is to prevent its diffusion out of the cell as the charged phosphate group prevents glucose 6-phosphate from easily crossing the cell membrane.
One sugar commonly used is glucose, often in the form of glucose tablets (glucose pressed into a tablet shape sometimes with one or more other ingredients as a binder), hard candy, or sugar packet. [103] When made from corn syrup, the final product is high-fructose corn syrup (HFCS). [82], The glucose in the blood is called blood sugar. [54] About 90% of kidney glucose reabsorption is via SGLT2 and about 3% via SGLT1. InChI=1S/C6H12O6/c7-1-2-3(8)4(9)5(10)6(11)12-2/h2-11H,1H2/t2-,3-,4+,5-,6?/m1/s1, C([C@@H]1[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]([C@H](O1)O)O)O)O)O, Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their, Classical qualitative detection reactions, Photometric enzymatic methods in solution. A solution with indigo carmine and sodium carbonate destains when boiled with glucose.[122]. [83] In addition, glucose in the brain binds to glucose receptors of the reward system in the nucleus accumbens. [104][105] Starting in 1982, pullulanases from Aspergillus niger were used in the production of glucose syrup to convert amylopectin to starch (amylose), thereby increasing the yield of glucose. In addition, glucose metabolites produce all nonessential amino acids, sugar alcohols such as mannitol and sorbitol, fatty acids, cholesterol and nucleic acids. PINs are not identified for natural products. [122] An alkaline bismuth solution is used to precipitate elemental, black-brown bismuth with glucose. Some of these polymers (starch or glycogen) serve as energy stores, while others (cellulose and chitin, which is made from a derivative of glucose) have structural roles. Encyclopedia.com. A systematic review", "Diagnosing Diabetes and Learning About Prediabetes", "An insulin index of foods: The insulin demand generated by 1000-kJ portions of common foods", "Pancreatic Regulation of Glucose Homeostasis", "A syn-ent-labdadiene derivative with a rare spiro--lactone function from the male cones of Wollemia nobilis", "Triterpene Saponins from the Roots ofIlex asprella", "High Fructose Corn Syrup: Questions and Answers", "A Glucose-Triptolide Conjugate Selectively Targets Cancer Cells under Hypoxia", Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft, "Ueber die Nachweisung des Traubenzuckers neben Dextrin und verwandten Krpern", "Review of glucose oxidases and glucose dehydrogenases: A bird's eye view of glucose sensing enzymes", Max Planck Institute of Molecular Plant Physiology, "Sweetening pharmaceutical radiochemistry by (18)f-fluoroglycosylation: A short review", Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase deficiency, Slavery in the British and French Caribbean, https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Glucose&oldid=1100590585, World Health Organization essential medicines, Articles with German-language sources (de), Short description is different from Wikidata, Chemical articles with multiple compound IDs, Multiple chemicals in an infobox that need indexing, Chemical articles with multiple CAS registry numbers, Pages using collapsible list with both background and text-align in titlestyle, Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes, Articles containing Ancient Greek (to 1453)-language text, Pages using multiple image with manual scaled images, All articles needing additional references, Articles needing additional references from April 2022, Wikipedia articles needing factual verification from April 2022, Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License 3.0, This page was last edited on 26 July 2022, at 18:19. [78][79][80][81] In the brain, which is dependent on glucose and oxygen as the major source of energy, the glucose concentration is usually 4 to 6mM (5mM equals 90mg/dL),[41] but decreases to 2 to 3mM when fasting. Over time the blood glucose levels should decrease as insulin allows it to be taken up by cells and exit the blood stream. The main reason for the immediate phosphorylation of glucose is to prevent its diffusion out of the cell as the charged phosphate group prevents glucose 6-phosphate from easily crossing the cell membrane.  Ultimately almost all biomolecules come from the assimilation of carbon dioxide in plants and microbes during photosynthesis.
Ultimately almost all biomolecules come from the assimilation of carbon dioxide in plants and microbes during photosynthesis. 
 [89] Eating or fasting prior to taking a blood sample has an effect on analyses for glucose in the blood; a high fasting glucose blood sugar level may be a sign of prediabetes or diabetes mellitus.[90]. Glucose is mainly used for the production of fructose and of glucose-containing foods. concanavalin A) as a receptor. Gluconeogenesis allows the organism to build up glucose from other metabolites, including lactate or certain amino acids, while consuming energy. [129][130] Given the importance of glucose analysis in the life sciences, numerous optical probes have also been developed for saccharides based on the use of boronic acids,[131] which are particularly useful for intracellular sensory applications where other (optical) methods are not or only conditionally usable. Glucose is the human body's key source of energy, through aerobic respiration, providing about 3.75kilocalories (16kilojoules) of food energy per gram. [97] Unbound glucose is one of the main ingredients of honey.
[89] Eating or fasting prior to taking a blood sample has an effect on analyses for glucose in the blood; a high fasting glucose blood sugar level may be a sign of prediabetes or diabetes mellitus.[90]. Glucose is mainly used for the production of fructose and of glucose-containing foods. concanavalin A) as a receptor. Gluconeogenesis allows the organism to build up glucose from other metabolites, including lactate or certain amino acids, while consuming energy. [129][130] Given the importance of glucose analysis in the life sciences, numerous optical probes have also been developed for saccharides based on the use of boronic acids,[131] which are particularly useful for intracellular sensory applications where other (optical) methods are not or only conditionally usable. Glucose is the human body's key source of energy, through aerobic respiration, providing about 3.75kilocalories (16kilojoules) of food energy per gram. [97] Unbound glucose is one of the main ingredients of honey.  The reagents are immobilised on a polymer matrix, the so-called test strip, which assumes a more or less intense color. [137] Also, the proportions of di- and trisaccharides can be quantified. Another enzyme, peroxidase, catalyzes a chromogenic reaction (Trinder reaction)[123] of phenol with 4-aminoantipyrine to a purple dye. For example, glucose concentrations in atmospheric air from inland China range from 0.8-20.1 pg/l, whereas east coastal China glucose concentrations range from 10.3-142 pg/l.[60]. [59] However, the glucose released in muscle cells upon cleavage of the glycogen can not be delivered to the circulation because glucose is phosphorylated by the hexokinase, and a glucose-6-phosphatase is not expressed to remove the phosphate group. Without it, glucose cannot enter the cell and therefore cannot be used as fuel for the body's functions. In principle, cellulose could be hydrolyzed to glucose, but this process is not yet commercially practical.[26]. Precious metals such as platinum or gold are used in electrodes, as well as carbon nanotube electrodes, which e.g. [82] Confusion occurs below 1mM and coma at lower levels. However, most glucose does not occur in its free form, but in the form of its polymers, i.e. [95] Insulin is a hormone that regulates glucose levels, allowing the body's cells to absorb and use glucose. [56] Glucose is also formed by the breakdown of polymeric forms of glucose like glycogen (in animals and mushrooms) or starch (in plants). in glycated hemoglobin. [122] With Hager's reagent, glucose forms mercury oxide during boiling. Liver cell glycogen can be converted to glucose and returned to the blood when insulin is low or absent; muscle cell glycogen is not returned to the blood because of a lack of enzymes. [117]. [126] CuCuO nanowires are also used as enzyme-free amperometric electrodes, reaching a detection limit of 50mol/L. The names of the degrading enzymes are often derived from the particular poly- and disaccharide; inter alia, for the degradation of polysaccharide chains there are amylases (named after amylose, a component of starch), cellulases (named after cellulose), chitinases (named after chitin), and more. [124], The electroanalysis of glucose is also based on the enzymatic reaction mentioned above.
The reagents are immobilised on a polymer matrix, the so-called test strip, which assumes a more or less intense color. [137] Also, the proportions of di- and trisaccharides can be quantified. Another enzyme, peroxidase, catalyzes a chromogenic reaction (Trinder reaction)[123] of phenol with 4-aminoantipyrine to a purple dye. For example, glucose concentrations in atmospheric air from inland China range from 0.8-20.1 pg/l, whereas east coastal China glucose concentrations range from 10.3-142 pg/l.[60]. [59] However, the glucose released in muscle cells upon cleavage of the glycogen can not be delivered to the circulation because glucose is phosphorylated by the hexokinase, and a glucose-6-phosphatase is not expressed to remove the phosphate group. Without it, glucose cannot enter the cell and therefore cannot be used as fuel for the body's functions. In principle, cellulose could be hydrolyzed to glucose, but this process is not yet commercially practical.[26]. Precious metals such as platinum or gold are used in electrodes, as well as carbon nanotube electrodes, which e.g. [82] Confusion occurs below 1mM and coma at lower levels. However, most glucose does not occur in its free form, but in the form of its polymers, i.e. [95] Insulin is a hormone that regulates glucose levels, allowing the body's cells to absorb and use glucose. [56] Glucose is also formed by the breakdown of polymeric forms of glucose like glycogen (in animals and mushrooms) or starch (in plants). in glycated hemoglobin. [122] With Hager's reagent, glucose forms mercury oxide during boiling. Liver cell glycogen can be converted to glucose and returned to the blood when insulin is low or absent; muscle cell glycogen is not returned to the blood because of a lack of enzymes. [117]. [126] CuCuO nanowires are also used as enzyme-free amperometric electrodes, reaching a detection limit of 50mol/L. The names of the degrading enzymes are often derived from the particular poly- and disaccharide; inter alia, for the degradation of polysaccharide chains there are amylases (named after amylose, a component of starch), cellulases (named after cellulose), chitinases (named after chitin), and more. [124], The electroanalysis of glucose is also based on the enzymatic reaction mentioned above.  For the increased uptake of glucose in tumors various SGLT and GLUT are overly produced.[70][71]. The first step of glycolysis is the phosphorylation of glucose by a hexokinase to form glucose 6-phosphate. [42] Approximately 180220g (6.37.8oz) of glucose is produced in the liver of an adult in 24 hours.
For the increased uptake of glucose in tumors various SGLT and GLUT are overly produced.[70][71]. The first step of glycolysis is the phosphorylation of glucose by a hexokinase to form glucose 6-phosphate. [42] Approximately 180220g (6.37.8oz) of glucose is produced in the liver of an adult in 24 hours.  The produced hydrogen peroxide can be amperometrically quantified by anodic oxidation at a potential of 600 mV. This complex of the proteins T1R2 and T1R3 makes it possible to identify glucose-containing food sources.
The produced hydrogen peroxide can be amperometrically quantified by anodic oxidation at a potential of 600 mV. This complex of the proteins T1R2 and T1R3 makes it possible to identify glucose-containing food sources.  Wenyue Kang and Zhijun Zhang (2020): "Selective Production of Acetic Acid via Catalytic Fast Pyrolysis of Hexoses over Potassium Salts", "glucose." Glucose is also added onto certain proteins and lipids in a process called glycosylation. Use of glucose as an energy source in cells is by either aerobic respiration, anaerobic respiration, or fermentation. [83][85] Insulin lowers the glucose level, glucagon increases it. Glucose is produced industrially from starch by enzymatic hydrolysis using glucose amylase or by the use of acids. In concentrated solutions of glucose with a low proportion of other carbohydrates, its concentration can be determined with a polarimeter. Glucose uptake in cells of organisms is measured with 2-deoxy-D-glucose or fluorodeoxyglucose. [122][verification needed] In a yeast solution, alcoholic fermentation produces carbon dioxide in the ratio of 2.0454 molecules of glucose to one molecule of CO2.
Wenyue Kang and Zhijun Zhang (2020): "Selective Production of Acetic Acid via Catalytic Fast Pyrolysis of Hexoses over Potassium Salts", "glucose." Glucose is also added onto certain proteins and lipids in a process called glycosylation. Use of glucose as an energy source in cells is by either aerobic respiration, anaerobic respiration, or fermentation. [83][85] Insulin lowers the glucose level, glucagon increases it. Glucose is produced industrially from starch by enzymatic hydrolysis using glucose amylase or by the use of acids. In concentrated solutions of glucose with a low proportion of other carbohydrates, its concentration can be determined with a polarimeter. Glucose uptake in cells of organisms is measured with 2-deoxy-D-glucose or fluorodeoxyglucose. [122][verification needed] In a yeast solution, alcoholic fermentation produces carbon dioxide in the ratio of 2.0454 molecules of glucose to one molecule of CO2.  In humans, about 70 genes are known that code for glycosidases. In dilute sodium hydroxide or other dilute bases, the monosaccharides mannose, glucose and fructose interconvert (via a Lobry de BruynAlberdaVan Ekenstein transformation), so that a balance between these isomers is formed. To monitor the body's response to blood glucose-lowering therapy, glucose levels can be measured. In the US, almost exclusively corn (more precisely, corn syrup) is used as glucose source for the production of isoglucose, which is a mixture of glucose and fructose, since fructose has a higher sweetening power with same physiological calorific value of 374 kilocalories per 100 g. The annual world production of isoglucose is 8 million tonnes (as of 2011). [38]:59 In humans, gluconeogenesis occurs in the liver and kidney,[58] but also in other cell types. [41], Many of the long-term complications of diabetes (e.g., blindness, kidney failure, and peripheral neuropathy) are probably due to the glycation of proteins or lipids.
In humans, about 70 genes are known that code for glycosidases. In dilute sodium hydroxide or other dilute bases, the monosaccharides mannose, glucose and fructose interconvert (via a Lobry de BruynAlberdaVan Ekenstein transformation), so that a balance between these isomers is formed. To monitor the body's response to blood glucose-lowering therapy, glucose levels can be measured. In the US, almost exclusively corn (more precisely, corn syrup) is used as glucose source for the production of isoglucose, which is a mixture of glucose and fructose, since fructose has a higher sweetening power with same physiological calorific value of 374 kilocalories per 100 g. The annual world production of isoglucose is 8 million tonnes (as of 2011). [38]:59 In humans, gluconeogenesis occurs in the liver and kidney,[58] but also in other cell types. [41], Many of the long-term complications of diabetes (e.g., blindness, kidney failure, and peripheral neuropathy) are probably due to the glycation of proteins or lipids.  g). Humans do not produce cellulases, chitinases, or trehalases, but the bacteria in the gut microbiota do. [ 1], Tumor cells often grow comparatively quickly and consume an above-average amount of glucose by glycolysis,[69] which leads to the formation of lactate, the end product of fermentation in mammals, even in the presence of oxygen. This negative spiral contributes to pancreatic burnout, and the disease progression of diabetes.
g). Humans do not produce cellulases, chitinases, or trehalases, but the bacteria in the gut microbiota do. [ 1], Tumor cells often grow comparatively quickly and consume an above-average amount of glucose by glycolysis,[69] which leads to the formation of lactate, the end product of fermentation in mammals, even in the presence of oxygen. This negative spiral contributes to pancreatic burnout, and the disease progression of diabetes.  With a high supply of glucose, the metabolite acetyl-CoA from the Krebs cycle can also be used for fatty acid synthesis. after overnight fasting, is about 70 to 100mg/dL of blood (4 to 5.5mM). It is used as an energy source in organisms, from bacteria to humans, through either aerobic respiration, anaerobic respiration (in bacteria), or fermentation. Other than its direct use as a monomer, glucose can be broken down to synthesize a wide variety of other biomolecules. [49] Glucose enters the liver via the portal vein and is stored there as a cellular glycogen. In addition, the values in the arterial blood are higher than the concentrations in the venous blood since glucose is absorbed into the tissue during the passage of the capillary bed. In an ammoniacal lead acetate solution, white lead glycoside is formed in the presence of glucose, which becomes less soluble on cooking and turns brown. [75] The high availability of carbohydrates from plant biomass has led to a variety of methods during evolution, especially in microorganisms, to utilize glucose for energy and carbon storage. [76], Glucose and oxygen supply almost all the energy for the brain,[77] so its availability influences psychological processes.
With a high supply of glucose, the metabolite acetyl-CoA from the Krebs cycle can also be used for fatty acid synthesis. after overnight fasting, is about 70 to 100mg/dL of blood (4 to 5.5mM). It is used as an energy source in organisms, from bacteria to humans, through either aerobic respiration, anaerobic respiration (in bacteria), or fermentation. Other than its direct use as a monomer, glucose can be broken down to synthesize a wide variety of other biomolecules. [49] Glucose enters the liver via the portal vein and is stored there as a cellular glycogen. In addition, the values in the arterial blood are higher than the concentrations in the venous blood since glucose is absorbed into the tissue during the passage of the capillary bed. In an ammoniacal lead acetate solution, white lead glycoside is formed in the presence of glucose, which becomes less soluble on cooking and turns brown. [75] The high availability of carbohydrates from plant biomass has led to a variety of methods during evolution, especially in microorganisms, to utilize glucose for energy and carbon storage. [76], Glucose and oxygen supply almost all the energy for the brain,[77] so its availability influences psychological processes.